Frequency Bands
Frequency bands provide a structure for the classification of electromagnetic waves based on frequency. Essentially, frequency bands allow us to subdivide the most common types of electromagnetic waves in a structure that is useful for radio communications. The classification system itself is called the radio spectrum.
The lowest frequency band (ITU Band 1) is called “Extremely Low Frequency” and includes waves that have frequencies between 3 and 30 Hz. The highest frequency band (ITU Band 12) is called “Tremendously High Frequency” and includes frequencies from 300 GHz to 3 THz.
Lower frequencies have longer wavelengths and lower energy, while higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths and higher energy.
This system is highly useful in radio and satellite communications. Electronics used in communications will typically have circuits that allow for tuning within or across bands using filter circuits.
Table of Radio Spectrum Frequency Bands
| Band Name | Abbreviation | Frequency | Wavelength | ITU Band |
| Extremely Low Frequency | ELF | 3 Hz – 30 Hz | 100 Mm – 10 Mm | 1 |
| Super Low Frequency | SLF | 30 Hz – 300 Hz | 10 Mm – 1 Mm | 2 |
| Ultra Low Frequency | ULF | 300 Hz – 3 kHz | 1 Mm – 100 km | 3 |
| Very Low Frequency | VLF | 3 kHz – 30 kHz | 100 km – 10 km | 4 |
| Low Frequency | LF | 30 kHz – 300 kHz | 10 km – 1 km | 5 |
| Medium Frequency | MF | 300 kHz – 3 MHz | 1 km – 100 m | 6 |
| High Frequency | HF | 3 MHz – 30 MHz | 100 m – 10 m | 7 |
| Very High Frequency | VHF | 30 MHz – 300 MHz | 10 m – 1 m | 8 |
| Ultra High Frequency | UHF | 300 MHz – 3 GHz | 1 m – 100 mm | 9 |
| Super High Frequency | SHF | 3 GHz – 30 GHz | 100 mm – 10 mm | 10 |
| Extremely High Frequency | EHF | 30 GHz – 300 GHz | 10 mm – 1 mm | 11 |
| Tremendously High Frequency | THF | 300 GHz – 3 THz | 1 mm – 100 µm | 12 |
Electromagnetic Frequency and Wavelength
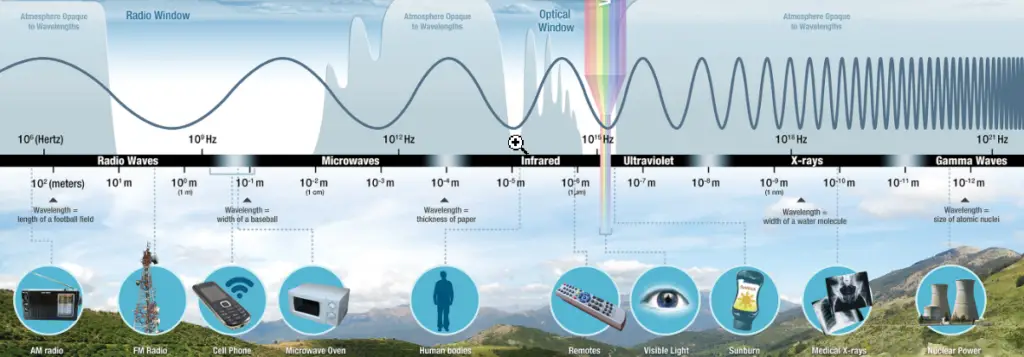
The frequency and wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is always linked by the speed of light:
Wavelength (λ) x Frequency (f) = Speed of Light (c)
λf = c
This is why the wavelength decreases as frequency is increased.
The energy of the wave is linearly proportional to the frequency. A constant is required for the two terms to equal each other. This is called Planck’s constant and is an important topic in physics:
Energy (E) = Frequency (f) x Planck’s constant (h)
E = hf