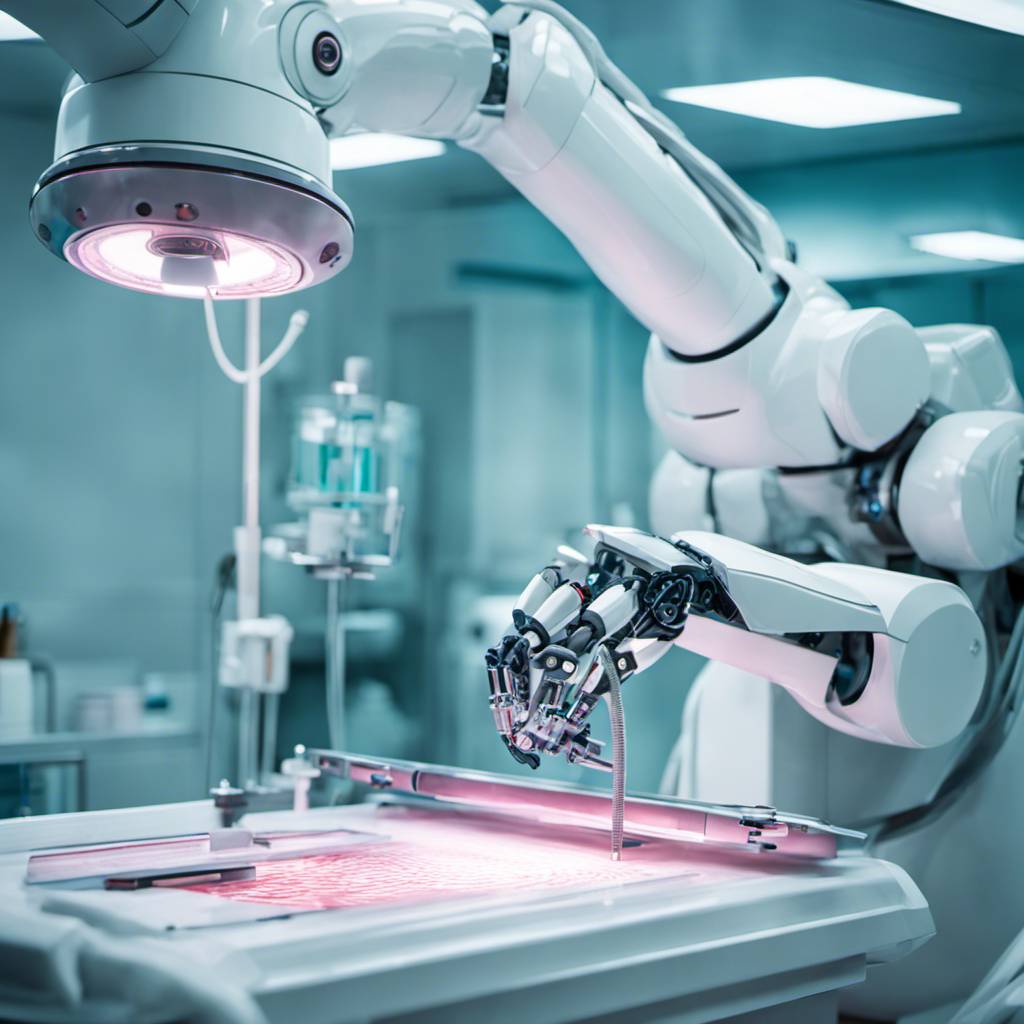
As the clock strikes 10 at the bustling Max Hospital, Saket, the Operating Room (OR) is a hive of activity. Surgeons bustle about, preparing for a series of surgeries. On the agenda for the day are two gall bladder removals and a hernia repair. One of the patients, a man in his forties, has been suffering from severe abdominal pain due to gallstones obstructing his bile duct.
At the helm of these surgeries is Dr Pradeep Chowbey, a luminary in the field of gastric surgery and the chairman of Max Institute of Laparoscopic, Endoscopic & Bariatric Surgery. His tool of choice for these procedures is the Versius, a cutting-edge surgical robotic system developed by CMR Surgical, a company based in Cambridge.
The Versius, with its surgical arms inserted into the patient’s body through small incisions, offers Dr Chowbey a detailed 3D image of the gallbladder and its surrounding areas on a large screen attached to the console. With his wrists resting on the console and his elbows supported, he navigates through the complex procedure. His task is to remove the gallbladder, which is nestled within fat deposits and surrounded by two major blood vessels.
With incredible precision, Dr Chowbey enlarges the area he needs to operate on, untangles and clips the blood vessels, and without disturbing the adjacent liver or making additional incisions, he excises the gallbladder and removes the troublesome gallstones. The entire procedure takes just ten minutes.
“The beauty of robots is that they provide me with a comprehensive 3D view of the organ,” says Dr Chowbey, “This allows me to operate without causing any damage to the surrounding tissue. The result? Quicker recovery times and significantly less pain compared to conventional and laparoscopic surgery.”
Robotic technology is transforming healthcare in India in ways never before imagined. These robots are not only reducing risks in complex surgeries but also assisting patients in their rehabilitation, dispensing medications, and even preventing falls when patients are alone.
According to a report by BIS Research, the Indian surgical robotics market is set to experience substantial growth, with an estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20% between 2017 and 2025. This growth is projected to result in a market value of $350 million, a significant increase from the $64.9 million in 2016.
The first surgical robot, Da Vinci, made by California-based company Intuitive, arrived at Apollo Hospital, Delhi in 2002. However, the widespread adoption of robotic surgeries in private hospitals in the National Capital Region (NCR) only began around 2015-2016.
Post-Covid, the adoption of robotic technology has accelerated across India. Mandeep Singh Kumar, Vice President and country GM, Intuitive Surgicals says, “The robotic-assisted surgery (RAS) market is rapidly expanding in India. The growth is driven by an increased interest among surgeons to adopt technology to deliver improved clinical and patient outcomes.”
India currently boasts over 800 robotic-assisted trained surgeons working across 125 plus da Vinci surgical programs focused on a wide range of specialties.
A typical robot used in abdominal surgeries features four arms. Three are dedicated to holding various surgical instruments, while the fourth is equipped with a 3D camera. The three instrument-holding arms are controlled by a computer and mimic the precise movements of the surgeon, who operates the system from a nearby console. The surgeon can closely monitor and control the surgical procedure on a high-definition 3D screen connected to the robotic system.
CMR Surgical launched its next-generation Versius in India in 2019. In just two years, the company has successfully deployed its robotic systems in 38 hospitals across India and has trained over 300 surgeons in robotic surgery.
“Robotic-assisted surgeries allow surgeons to perform more procedures in a shorter amount of time, increasing the capacity of healthcare facilities to serve more patients,” says Dr Chowbey. Patients also benefit as surgical robots enable minimally invasive procedures, resulting in shorter hospital stays, reduced recovery times, and lower healthcare costs.
With the advent of electronics, computers, programming languages, and coding, the healthcare industry in India is witnessing a revolution. Robots are not only being used for surgeries but also for tasks like drug dispensing, laboratory analysis, and sterilization. They can operate in difficult-to-reach areas in the human body, making them invaluable tools in the medical field.
The future of healthcare in India looks promising with the adoption of such advanced technology. As we move forward, the integration of robotics in healthcare is expected to become even more seamless, leading to improved patient outcomes and overall healthcare delivery.