TryHackMe – Windows Fundamentals 3 – Complete Walkthrough

Windows Fundamentals 3 is the third room in the ‘Windows Fundamentals’ series on TryHackMe.
It introduces a number of security-related tools including Windows Update, Microsoft Defender antivirus, firewall and SmartScreen, Trusted Platform Module (TPM), BitLocker, and Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS).
About This Walkthrough:
In my walkthroughs I try to provide a unique perspective into the topics covered by the room. Sometimes I will also review a topic that isn’t covered in the TryHackMe room because I feel it may be a useful supplement.
I try to prevent spoilers by making finding the solutions a manual action, similar to how you might watch a video of a walkthrough; they can be found in the walkthrough but require an intentional action to obtain. Always try to work as hard as you can through every problem and only use the solutions as a last resort.
This room can be found at: https://tryhackme.com/room/windowsfundamentals3xzx
- TryHackMe – Windows Fundamentals 3 – Complete Walkthrough
Walkthrough
Task 1 – Introduction
This room is the third part in the Windows Fundamentals series.
Use the green ‘Start Machine’ button to launch the Windows VM for this room.
Question 1
Read above and start the virtual machine.
Answer:
No answer needed
Task 2 – Windows Updates
Have you ever been in the middle of something important when Windows barged in, forcing you to update? Updates might occasionally be inconvenient but they’re also super important.
Microsoft provides Windows updates on the 2nd Tuesday of the month, called ‘Patch Tuesday‘. But if an update is urgent, they might not wait for the next Patch Tuesday before rolling it out.
There is also a utility called Windows Update, which has options for scheduling updates and viewing update history among others.
If you push off updates for long enough, Windows may force you to restart your computer.
Question 1
There were two definition updates installed in the attached VM. On what date were these updates installed?
Walkthrough:
Access Windows Updates on the VM using Settings or the Start Menu search box.
Click on ‘View update history’:
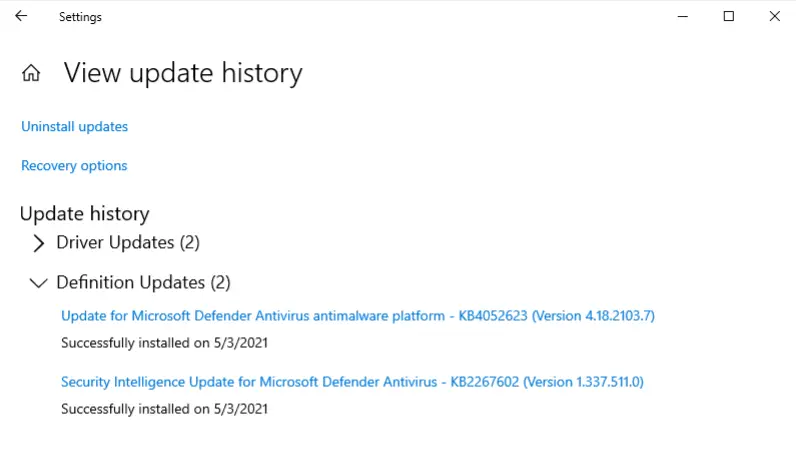
Under the ‘Definition Updates’ category, you should see two updates that were successfully started on the same day.
Answer:
(Highlight below to see the answer):
5/3/2021
Task 3 – Windows Security
Windows includes a utility for managing security, aptly named Windows Security.
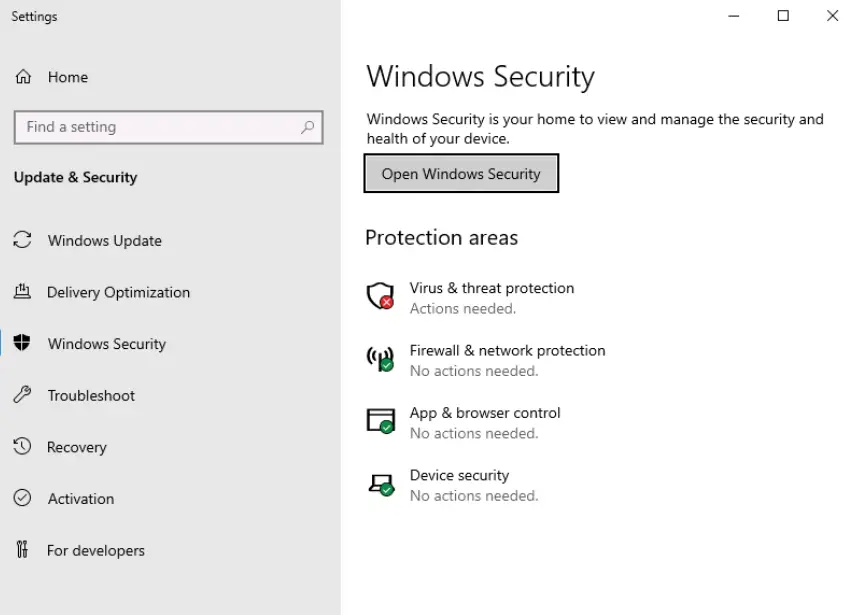
This utility gives you a dashboard where you can quickly review any outstanding issues and assess how critical they are using the green, yellow, and red color coding.
There are links allowing you to access many different security features including virus and threat protection and the Defender firewall.
Question 1
In the above image, which area needs immediate attention?
Walkthrough:
The need for attention is signaled via color-coding.
Answer:
Virus & threat protection
Task 4 – Virus & Threat Protection
Windows has a built-in Virus scanner called Microsoft Defender. Microsoft Defender can be managed via the virus and threat protection utility.
The current threats area allows you to see the results of the latest scan, if there are any current threats that need to be resolved, and options for scanning.
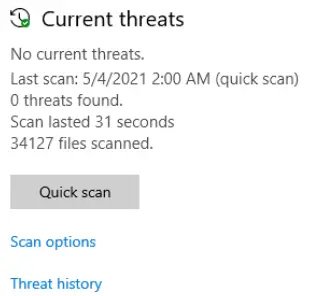
Scanning options include quick, full, custom, and offline. Quick scan is a great starting point, as it will generally tell you if a full scan is needed. The offline scan can also be useful if you’re concerned about infection with a virus or malware.
There are lots of settings, which are located under ‘Manage Settings’. Real-time protection prevents viruses or malware from executing. It only works when it’s turned on. Cloud-delivered protection allows Microsoft to query a database in the cloud to quickly assess any suspect code found on your system. This improves speed and robustness.
To learn more, I recommend reading Microsoft’s support page.
Question 1
Specifically, what is turned off that Windows is notifying you to turn on?
Walkthrough:
In the last task, we saw on the Windows Security dashboard that action is needed in the category of Virus & Threat Protection.
You can find more details on the dashboard in Virus & Threat Protection:
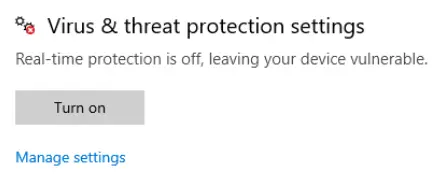
Answer:
Real-time protection
Task 5 – Firewall & Network Protection
Windows has a built-in firewall to help protect networks and devices. The firewall operates using three network profiles: domain, private network, and public network.
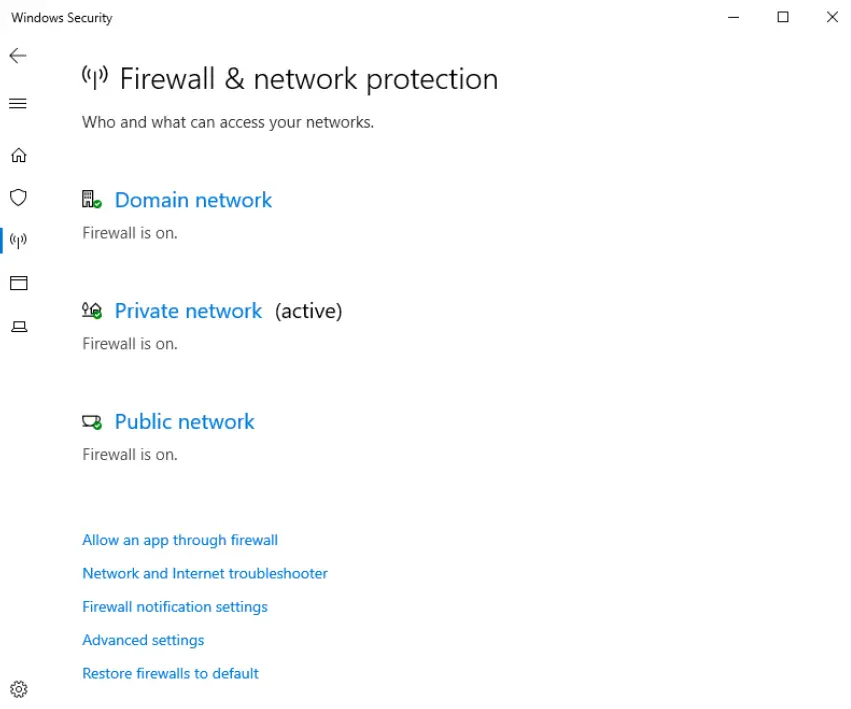
The firewall is very simple to use: options including turning each profile firewall on or off, blocking all incoming connections, and using custom rules to allow specific connections.
Question 1
If you were connected to airport Wi-Fi, what most likely will be the active firewall profile?
Walkthrough:
This question is used to demonstrate the reason for having different firewall profiles.
Of the three options (domain, private, public), which one best describes airport Wi-Fi?
Answer:
(Highlight below to see the answer):
Public network
Task 6 – App & Browser Control
The App & Browser Control utility helps to supplement the Virus scanner in protecting against malware. The two main categories are check apps and files (or reputation-based protection), and exploit protection.
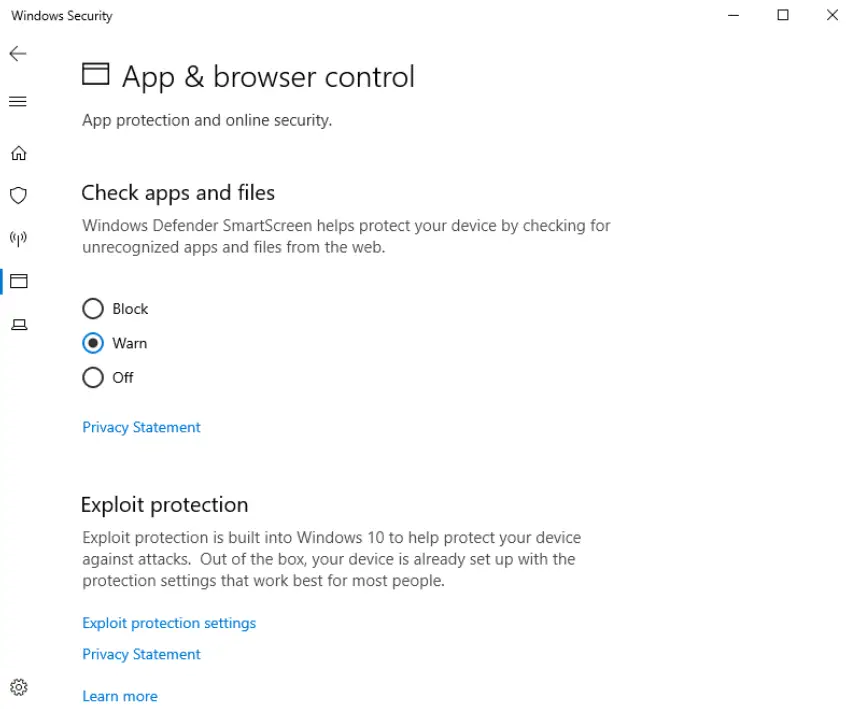
The ‘check apps and files’ feature uses Microsoft Defender SmartScreen to check unrecognized apps and files. It produces a warning anytime you may be downloading or running potential malware.
Exploit protection prevents a number of attacks, providing an extra defense against specific exploits.
Question 1
Read the above.
Answer:
No answer needed
Task 7 – Device Security
Device Security is used to manage security options to protect the device against malicious software. There are only a few options available in Device Security, and these are rarely touched.
Core isolation is used to isolate processes from the OS. The main option for core isolation is memory integrity. This allows Windows to use Hyper-V hardware virtualization to essentially create a virtual machine (VM) that remains isolated in computer memory, protecting it against attacks.
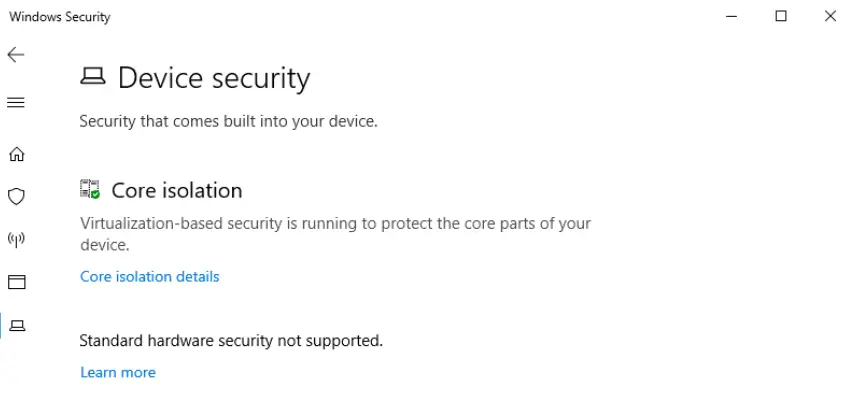
Some computers have a chip called a security processor, or, more specifically, a Trusted Platform Module (TPM).
A TPM is a computer chip used to perform cryptographic operations. Systems with a TPM will also see details about their security processor in the Device Security tool.
Question 1
What is the TPM?
Answer:
Trusted Platform Module
Task 8 – BitLocker
BitLocker is used to prevent data exposure on lost or stolen computers. It is best used with a TPM (security processor).
You can use BitLocker on a system without a TPM, but this requires inserting a USB key on startup or when resuming from hibernation.
Question 1
What must a user insert on computers that DO NOT have a TPM version 1.2 or later?
Answer:
USB startup key
Task 9 – Volume Shadow Copy Service
In order to ensure a successful backup and/or restore operations, coordination has to take place between different entities: the application performing the backup, the applications being backed up, and the storage processes.
Microsoft created the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to handle this coordination. VSS was introduced with Windows Server 2003, and can backup application data without taking the application offline.
Malware writers are often aware of VSS and have ways of getting around it. For this reason, it’s important to have offline backups available.
Question 1
What is VSS?
Answer:
Volume Shadow Copy Service
Task 10 – Conclusion
This room tackled a number of security tools that come packaged with the Windows OS.
Question 1
Read the above.
Answer:
No answer needed
Conclusion
The is the third of the Windows Fundamentals series, and does a good job of introducing Windows security options at a very high level. Personally this is not my favorite THM room, as it has no real interactivity and introduces the topics at about the same level as you would get by simply navigating to the tools and reading the options. But it does a good job of providing an overview.
Overall, I thought this room was a useful addition. A huge thanks to heavenraiza for putting this room together!